News:
When Should a Museum Return Looted Items? It’s Complicated.
By Nina Siegal
A Dutch exhibition brings together items taken in colonial times, by Napoleon’s army and by the Nazis to argue there isn’t one solution to restitution.
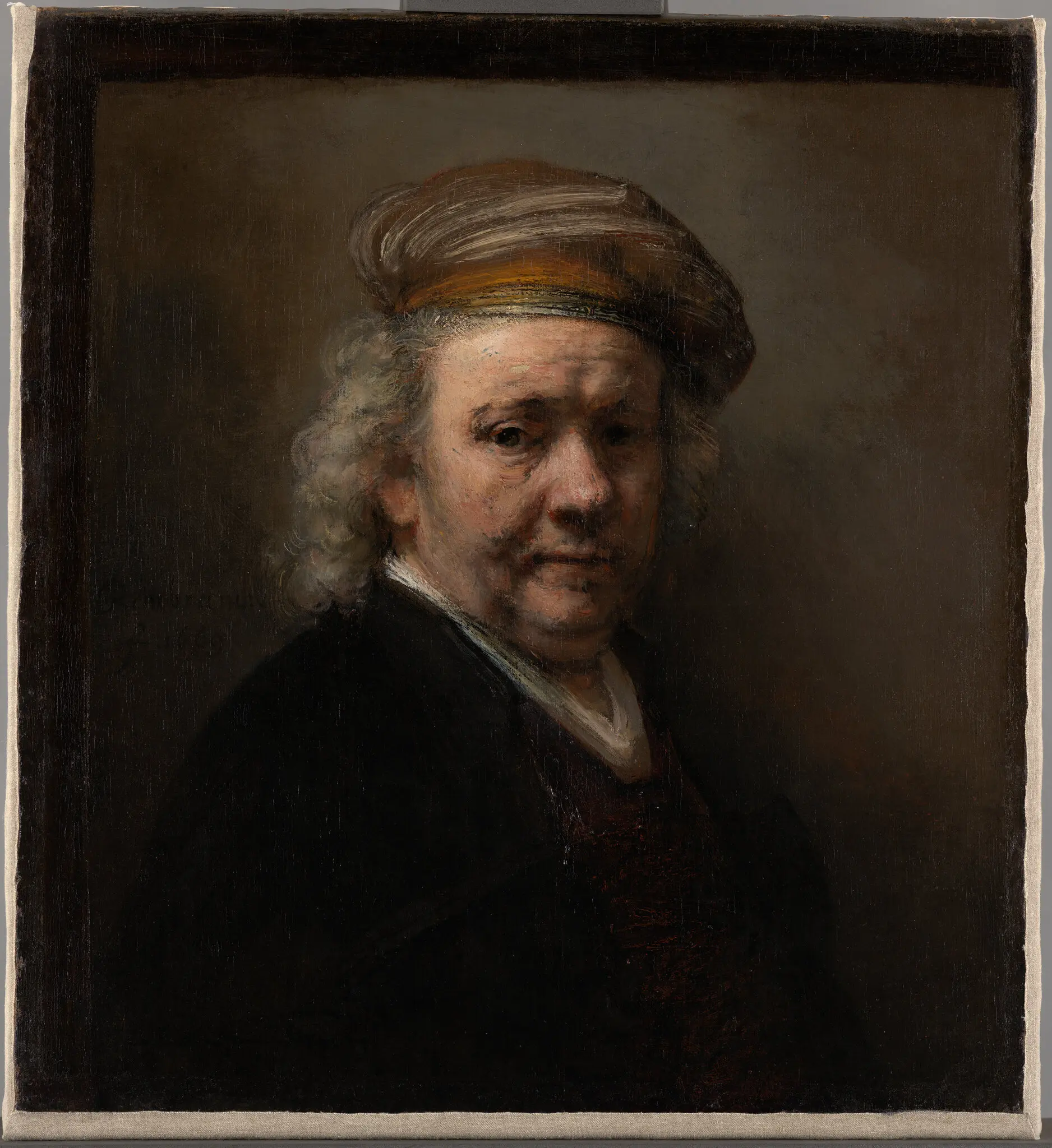

The show “Loot: 10 Stories” at the Mauritshuis features a 1669 Rembrandt self-portrait that was stolen by the Nazis from a Jewish family and stored in a salt mine during World War II
Some museums contain artworks that were looted by the Nazis during World War II. Others have amassed collections of objects stolen by colonial powers. Yet others saw their own collections plundered as the spoils of war.
The Mauritshuis in The Hague has it all.
Founded in the 17th century by a Dutch prince who governed a colony in what is now Brazil, the museum once held many so-called “ethnographic” objects in its “cabinet of curiosities.” During the Napoleonic era, the French army stole its entire painting collection. And the Mauritshuis still holds two dozen works identified as Nazi-looted art, for which rightful owners have not been found.
“The whole history of the museum is very closely related to war booty and looted art,” said the Mauritshuis’s director, Martine Gosselink, which is why she decided to mount, “Loot: 10 Stories,” an exhibition running through Jan. 7, 2024, that explores the history of dubious museum acquisitions.
“We want to show that there’s no one-size-fits-all solution,” Gosselink said. “Every case has its own history, every object has its own biography, and every object needs its own approach.”
In a single room, the museum presents 10 objects, or groups of objects, each of which is linked to a nefarious past. Two guest curators, Eline Jongsma and Kel O’Neill, have developed virtual reality presentations and short documentary films to help visitors inhabit the items’ histories.
Putting on a VR headset and looking at a Rembrandt self-portrait from 1669, for example, visitors virtually enter an Austrian salt mine, where Nazis hid stolen art during World War II. The Rembrandt was taken in 1940 from the Rijksmuseum, where it had been on loan from a German-Jewish family. Hitler planned to hang it in a museum of his spoils, the Führermuseum. After the war, it was returned to the family and sold to the Mauritshuis.
The Rembrandt restitution was a clear-cut case, O’Neill explained, but others have proven far more difficult.
“There is a continuum,” he said. “On the other end of the continuum, there are objects that have been looted that perhaps people don’t want back.”
In one VR experience, visitors are taken into a recreation of a temple on the island of Bali, Indonesia, where a dead soldier is seen clutching an ornate dagger, known as a kris. It was stolen from an unknown warrior during a battle in 1849.
Just two years later, a German collector gave the kris to the King of Prussia for his art chamber, which would later become part of the Ethnological Museum of Berlin. Krisses are considered spiritual objects in Bali, the wall text at the Mauritshuis explains, but no one has sought the return of this object, perhaps because, taken out of its context, the kris has lost its meaning.
Jongsma and O’Neill traveled to Bali earlier this year and presented the kris to King of Klungkung, Ida Dewa Agung Istri Kanya, but he didn’t want it, because he didn’t feel a connection to it.
“That blew away some of my assumptions,” O’Neill said.
Important recent exhibitions at European museums have focused on colonial pillage, Napoleon’s plunder and Nazi-looted art, but it is rare to see all three featured in a single show. Some experts in restitution questioned the idea of combining them, which could suggest the histories are equal.
“You shouldn’t mix them up in a great melting pot,” said Gilbert Lupfer, the executive chairman of the German Lost Art Foundation. “For centuries, art was looted in times of crisis and times of war, and that’s nothing new. But Nazi looting and Napoleonic looting are not the same.”
When the Nazis looted art in Germany, it “was part of the Holocaust,” he said. “That was not just a phenomenon of making money with art works from Jewish collections. It was part of the idea to destroy each form of Jewish life.” The key to making such an exhibition work, Lupfer added, would be to provide adequate context around such specifics.
Gosselink said while other shows went deeply into the context of each history, this show aimed to expose the differences. “The point is that these are not comparable,” she said. “The one and only comparison to be made is that they’re all looted.”
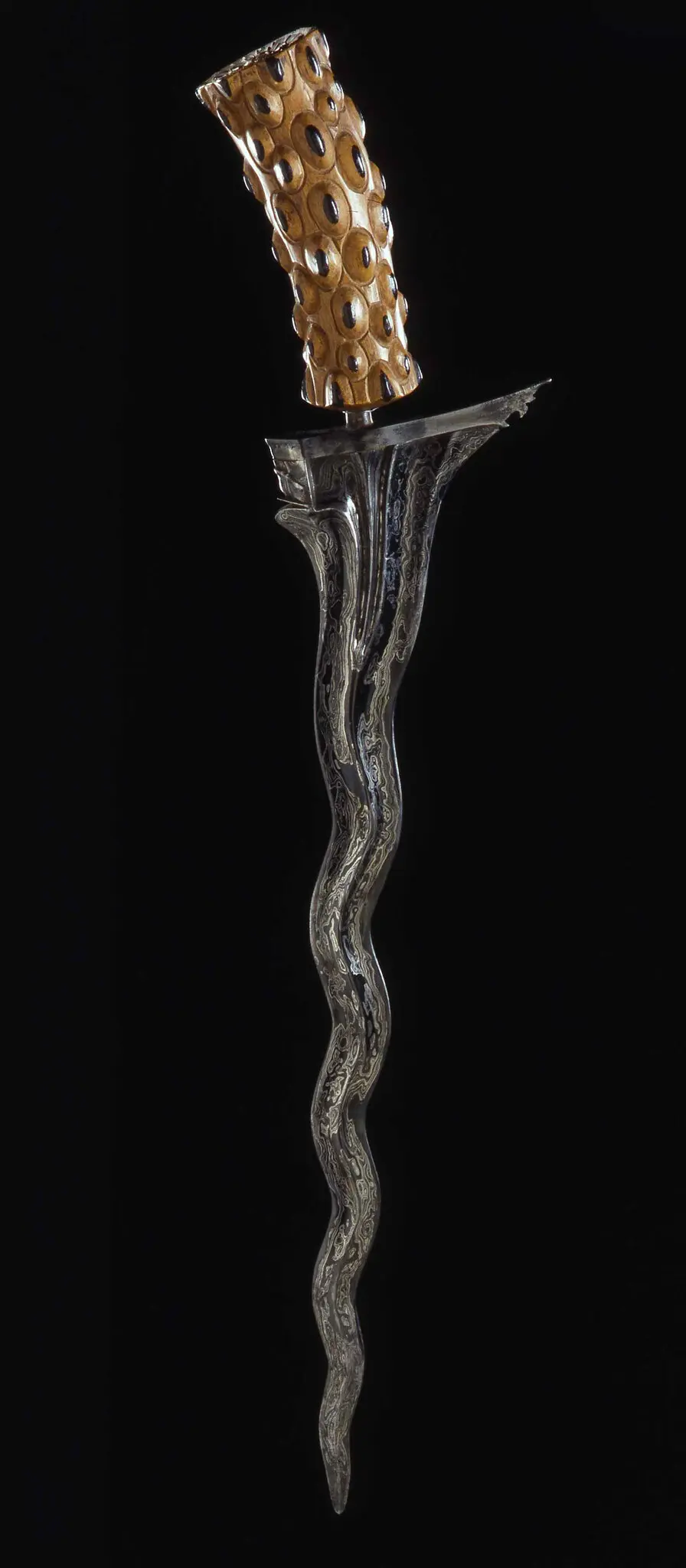
A Balinese dagger, known as a kris, that was stolen from an unknown warrior during a battle in 1849 and given to the king of Prussia.

A staff in the shape of a female figure is one of thousands of objects taken from the Maroon people of Suriname during Dutch colonial times.
Arthur Brand, an independent Dutch detective who handles many cases of stolen art, said he thought that combining these histories was an innovative approach, because too often people take polarizing, extreme views on restitution.
“Some say everything should go back, and then on the other hand there are people who say let’s not give anything back,” he said. “The Mauritshuis is trying to get everyone on board and get everyone involved in this topic, to see if there’s a middle path.”
But how can anyone request restitution of an object that’s been in a museum depot for so long that its rightful owners don’t know its missing? A simple staff in the shape of a female figure, owned by the Humboldt Forum, in Berlin, represents thousands of objects taken from the Maroon people of Suriname during Dutch colonial times. Little is known about the staff’s history except that it came taken from the Ndyuka community there.
Jongsma and O’Neill got in touch with Onias Landveld, a Surinamese poet linked to the Ndyukas, and recorded his visit to see the object. A museum curator removed it from a vitrine and allowed Landsveld to hold it in his hands. “Why is this still here?” Landsveld asked in a video of the encounter that is part of the Maurithuis show. “It felt like they had me and my culture on display, like I was extinct,” he said.
A museum curator asked him where he thought the staff should go. “I wanted to tell her: just wrap it up and give it to me,” he said. “I’ll bring it back; I’ll find a place.”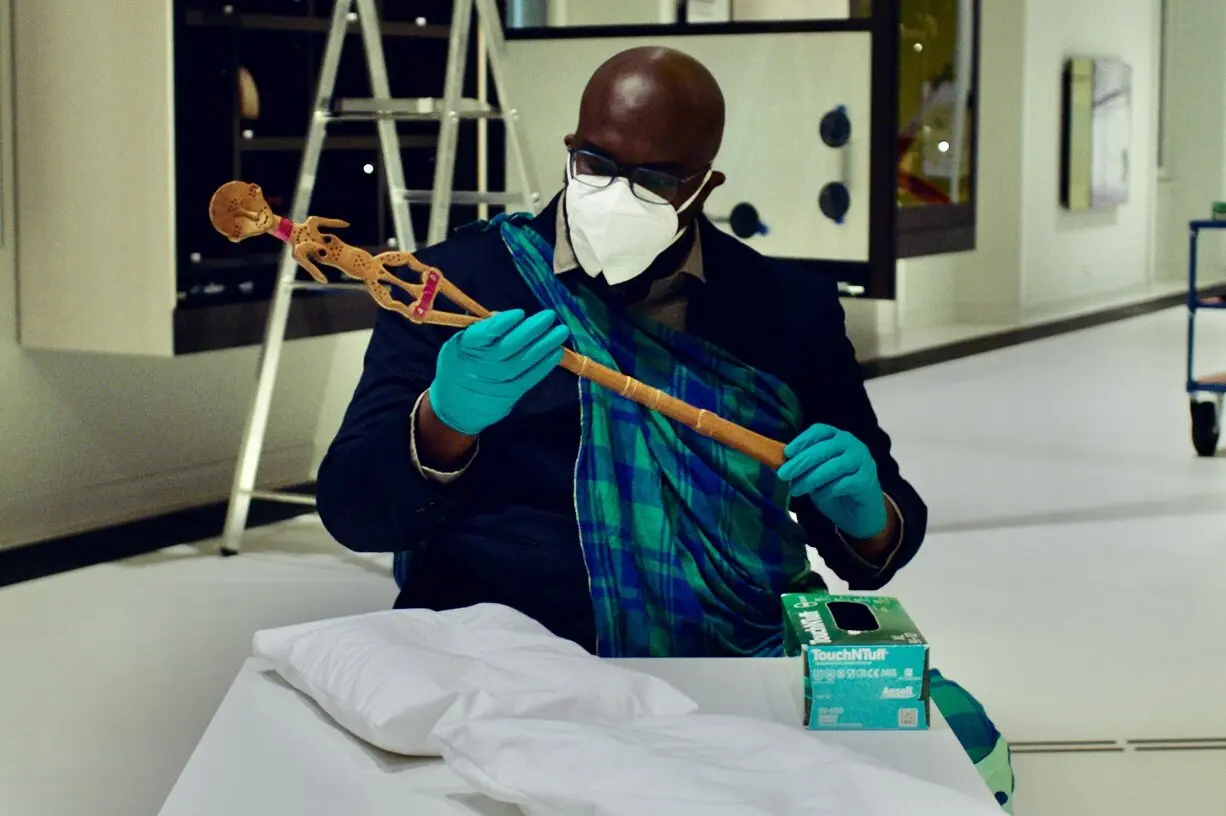
In a video in the exhibition, the Surinamese poet Onias Landveld holds a staff in the shape of a female figure that was taken from the Maroon people of Suriname during Dutch colonial times
Of course, Landsveld is aware that restitution is never so straightforward. No one has yet made an official claim on the staff, said O’Neill, “but if there is one, there will be a long political and personal journey.” He added, “I do think that opening up that conversation, wherever it leads, is necessary, and a central goal of this exhibition.”


